In the intricate world of manufacturing, precision is paramount. One tool that plays a critical role in ensuring this precision is the fixed limit gauge. This blog post will delve into the world of fixed limit gauges, explaining what they are, how they function, and their significance in part inspection.
What is a Fixed Limit Gage?
Fixed limit gauges, also known as fixed limit gages, are precision tools used in manufacturing to verify the dimensions and geometries of parts. Unlike other measuring devices, these gauges do not provide actual dimension values. Instead, their purpose is to ascertain whether a component falls within predetermined tolerance limits.
The Philosophy Behind Fixed Limit Gaging
The core idea of fixed limit gauging is not just to accept good parts but also to potentially reject parts that are near the extreme limits of tolerance. This strategy ensures that only components that meet strict quality standards pass the inspection. If a part is rejected by a fixed limit gauge, it can be re-measured using more accurate methods to determine its compliance with tolerance requirements.
Types of Fixed Limit Gages
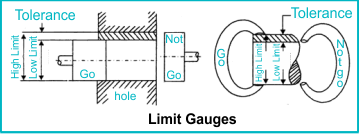
There are primarily two types of fixed limit gauges:
- Double-End Gages: These gauges have a 'go' member on one end and a 'no-go' member on the other. The 'go' member should fit within or over an acceptable workpiece, while the 'no-go' member should not.
- Progressive Gages: These are not mentioned in the draft but are important in the context of fixed limit gauges. Progressive gauges combine the 'go' and 'no-go' members in a single unit, allowing for a quicker inspection process but with less distinction between the near-minimum and near-maximum part sizes.
The Go/NoGo Concept in Plug Gages
A crucial aspect of fixed limit gaging is the Go/NoGo principle, particularly in plug gauges. The Go plug, with a plus tolerance, is designed to gauge the smallest acceptable hole size. Conversely, the NoGo plug, with a negative tolerance, gauges the largest acceptable hole size. In practice, a Go gauge should pass through the hole, while a NoGo gauge should not.
Why Fixed Limit Gages are Essential
Fixed limit gauges are indispensable in manufacturing for several reasons:
- Quality Assurance: They ensure that parts meet the required specifications and tolerances.
- Efficiency: They provide a quick and effective method for checking parts, especially in high-volume production.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By identifying out-of-tolerance parts early in the production process, they help reduce waste and save costs.
- Standardization: They provide a consistent and standardized method for quality control across various manufacturing stages.
FAQs
Q: How do I choose the right fixed limit gage for my application? A: The choice depends on the specific dimensions and tolerances of the parts you are inspecting. Consider the material, size, and tolerance requirements of your components to select the most appropriate gauge.
Q: Can fixed limit gages wear out? A: Yes, like all precision instruments, fixed limit gauges can wear out over time. Regular calibration and maintenance are essential to ensure their accuracy.
Q: Are fixed limit gages suitable for all types of materials? A: While they are versatile, the material of the part can affect the choice of gauge. For instance, softer materials might require different gauging techniques compared to harder materials.
Conclusion
Fixed limit gages are a fundamental tool in the manufacturing industry, vital for ensuring the precision and quality of parts. Understanding their function, types, and application is crucial for any professional in the field of manufacturing and quality control. By adhering to the principles of fixed limit gauging, manufacturers can maintain high standards of quality, efficiency, and reliability in their products.


